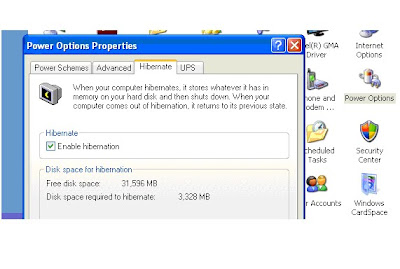
1. Hibernate shortcut -> Please make sure you have Hibernate turned on.
2. Go to the Control panel then click Performance and maintenance. Next, choose Power options, and select the hibernate tab.
3. Finally, make sure Enable hibernation is checked.
4. Please make the shortcut right click your desktop and choose New | Shortcut. Next, type this case-sensitive command into the dialog box rundll32.exe PowrProf.dll, SetSuspendState
5. click next. Give the shortcut a name and click finish.
6. From now on all you need to do to enter hibernation is double click the shortcut.
Monday, October 17, 2011
Thursday, April 7, 2011
xml file tokenizing in c coding
//header files
# include "stdio.h"
# include "string.h"
# include "stdlib.h"
//FunctionDeclaration
int YourFunction(char**,char*,char*);
//Global variable
char *cPagexml = "<root><device><producer>Indian politician</producer><problem>barrier for india's growth </problem></device></root>";
int main()
{
//Variable Declaration
char *TagName = "producer";
char *xml = NULL;
char *Tagvalue = "public must react about it";
//Memory allocation
xml = (char *)calloc(1024,1);
//To copy the xml file
strcpy(xml,cPagexml);
printf("Fist Time : %s\n\n\n",xml);
//Call function
YourFunction(&xml,TagName,Tagvalue);
printf("After your function : %s\n\n\n\n",xml);
return 0;
}
/****************************** function definition ****************************************
User want to write this function to get the output
***********************************************************************************************/
int YourFunction(char**xml,char*TagName,char*TagValue)
{
//Variable declartion
int nCount,nLoop;
int nTagValueLength;
int nLength;
char *cTempdata = (char *)calloc(1024,1);
char *cTemp = (char *)calloc(1024,1);
char *tempvalue=NULL;
// To move the pointer to producer
cTemp = strstr(*xml, TagName);
//To count the number of character pointer moved
nCount = (int)( cTemp - *xml);
// Cut the first ncount char from source
strncpy(cTempdata,*xml,nCount);
//to assign to other variable
nLoop = nCount;
// To reach the crrent position as tag
while(nLoop != 0)
{
nLoop--;
*cTempdata++;
}
// to reach the end of the tag name
while (*cTemp != '>')
{
// to assign in new pointer
*cTempdata++ = *cTemp++;
nCount++;
}
//for > symbol
*cTempdata++ = *cTemp++;
nCount++;
tempvalue = strstr(cTemp,TagName);
nTagValueLength = strlen(TagValue);
nLength = tempvalue - cTemp;
nLength -=2; //for </ symbols of end tag
if(nTagValueLength <= nLength)
{
while (*TagValue != '\0')
{
*cTempdata++ = *TagValue++;
*cTemp++;
++nCount;
}
nLength = (nLength-nTagValueLength);
while (nLength !=0)
{
nLength--;
*cTemp++;
}
}
else
{
while (*TagValue != '\0')
{
*cTempdata++ = *TagValue++;
++nCount;
}
while(nLength-- != 0)
*cTemp++;
}
while (*cTemp != '\0')
{
*cTempdata++ = *cTemp++;
nCount++;
}
// for reassigning the contents
nLoop = nCount;
while (nLoop--!= 0)
{
cTempdata--;
}
// To reassign the value to xml pointer
strcpy(*xml,cTempdata);
return 0;
}
OUTPUT:
Fist Time : <root><device><producer>Indian politician</producer><problem>barrier for india's growth </problem></device></root>
After your function : <root><device><producer>public must react about it</producer><problem>barrier for india's growth </problem></device></root>
Press any key to continue . . .
Indian Economy: Performance and Policies
# include "stdio.h"
# include "string.h"
# include "stdlib.h"
//FunctionDeclaration
int YourFunction(char**,char*,char*);
//Global variable
char *cPagexml = "<root><device><producer>Indian politician</producer><problem>barrier for india's growth </problem></device></root>";
int main()
{
//Variable Declaration
char *TagName = "producer";
char *xml = NULL;
char *Tagvalue = "public must react about it";
//Memory allocation
xml = (char *)calloc(1024,1);
//To copy the xml file
strcpy(xml,cPagexml);
printf("Fist Time : %s\n\n\n",xml);
//Call function
YourFunction(&xml,TagName,Tagvalue);
printf("After your function : %s\n\n\n\n",xml);
return 0;
}
/****************************** function definition ****************************************
User want to write this function to get the output
***********************************************************************************************/
int YourFunction(char**xml,char*TagName,char*TagValue)
{
//Variable declartion
int nCount,nLoop;
int nTagValueLength;
int nLength;
char *cTempdata = (char *)calloc(1024,1);
char *cTemp = (char *)calloc(1024,1);
char *tempvalue=NULL;
// To move the pointer to producer
cTemp = strstr(*xml, TagName);
//To count the number of character pointer moved
nCount = (int)( cTemp - *xml);
// Cut the first ncount char from source
strncpy(cTempdata,*xml,nCount);
//to assign to other variable
nLoop = nCount;
// To reach the crrent position as tag
while(nLoop != 0)
{
nLoop--;
*cTempdata++;
}
// to reach the end of the tag name
while (*cTemp != '>')
{
// to assign in new pointer
*cTempdata++ = *cTemp++;
nCount++;
}
//for > symbol
*cTempdata++ = *cTemp++;
nCount++;
tempvalue = strstr(cTemp,TagName);
nTagValueLength = strlen(TagValue);
nLength = tempvalue - cTemp;
nLength -=2; //for </ symbols of end tag
if(nTagValueLength <= nLength)
{
while (*TagValue != '\0')
{
*cTempdata++ = *TagValue++;
*cTemp++;
++nCount;
}
nLength = (nLength-nTagValueLength);
while (nLength !=0)
{
nLength--;
*cTemp++;
}
}
else
{
while (*TagValue != '\0')
{
*cTempdata++ = *TagValue++;
++nCount;
}
while(nLength-- != 0)
*cTemp++;
}
while (*cTemp != '\0')
{
*cTempdata++ = *cTemp++;
nCount++;
}
// for reassigning the contents
nLoop = nCount;
while (nLoop--!= 0)
{
cTempdata--;
}
// To reassign the value to xml pointer
strcpy(*xml,cTempdata);
return 0;
}
OUTPUT:
Fist Time : <root><device><producer>Indian politician</producer><problem>barrier for india's growth </problem></device></root>
After your function : <root><device><producer>public must react about it</producer><problem>barrier for india's growth </problem></device></root>
Press any key to continue . . .
Indian Economy: Performance and Policies
Thursday, March 31, 2011
Operator Overloding sample program in C++
/* Write a function, fn(), to increment the values of two variables of type int that are passed by reference.
*/
# include "stdio.h"
# include "iostream"
using namespace std;
class Reference
{
private:
int nVar1;
int nVar2;
public:
// constructor
Reference()
{
nVar1=0;
nVar2=0;
}
//to display the content
void Assign()
{
printf("%d\t%d\n", nVar1,nVar2);
}
//Operator overloading
void operator++()
{
nVar1++;
nVar2++;
nVar2++;
}
};
int main()
{
Reference Obj;
Obj.Assign();
Obj++;
Obj.Assign();
return 0;
}
OUTPUT:
0 0
1 2
Press any key to continue . . .
*/
# include "stdio.h"
# include "iostream"
using namespace std;
class Reference
{
private:
int nVar1;
int nVar2;
public:
// constructor
Reference()
{
nVar1=0;
nVar2=0;
}
//to display the content
void Assign()
{
printf("%d\t%d\n", nVar1,nVar2);
}
//Operator overloading
void operator++()
{
nVar1++;
nVar2++;
nVar2++;
}
};
int main()
{
Reference Obj;
Obj.Assign();
Obj++;
Obj.Assign();
return 0;
}
OUTPUT:
0 0
1 2
Press any key to continue . . .
Wednesday, March 30, 2011
What is Friend Function in C++?
A non_member function that is allowed access to the private variable f a class is called a FRIEND of the class.
Features of the friend function
1. A friend function can access the private member of a class.
2. Friend functions need not have a "this" pointer, as it does not belong to any object.
3. The friend declaration is unaffected by its location in the class.
4. the definition of a friend function does not require the class name with the scope resolution operator prefixed to it, as it is required for a class member function.
Unix Shell Programming
Let Us C
Features of the friend function
1. A friend function can access the private member of a class.
2. Friend functions need not have a "this" pointer, as it does not belong to any object.
3. The friend declaration is unaffected by its location in the class.
4. the definition of a friend function does not require the class name with the scope resolution operator prefixed to it, as it is required for a class member function.
Unix Shell Programming
Let Us C
What is Static Function in C++?
Declaring a member STATIC function restricts its scope and makes it independent of the individual objects of the class. This feature is useful for member functions as for data members. The static data type variable can be manipulated only by the static member of its class without affecting the rest of the program.
1. This function i not having the this pointer.
2. Object.function() is not used as SYNTAX.
3. If we want to access the static function, Then we go for class_Specifier::function();
1. This function i not having the this pointer.
2. Object.function() is not used as SYNTAX.
3. If we want to access the static function, Then we go for class_Specifier::function();
Tuesday, March 29, 2011
Compare unsinged long int and int in MSVC
# include "stdio.h"
int main()
{
int a;
unsigned long int b=0;
printf("Enter the integer vlue\n");
scanf("%d",&a);
printf("%d\t",a);
//printf("%d\t",b);
b = a;
printf("%u\t\n",b);
scanf("%d",&b);
printf("\n%u\t",b);
//printf("%d\t",a);
a = b;
printf("%d\t",a);
return 0;
}
OUTPUT
Enter the integer value
55555555555555555555555555555555555555555
a= -477218589 b= 3817748707
55555555555555555555555555555555555555555
a= -477218589 b= 3817748707 Press any key to continue . . .
int main()
{
int a;
unsigned long int b=0;
printf("Enter the integer vlue\n");
scanf("%d",&a);
printf("%d\t",a);
//printf("%d\t",b);
b = a;
printf("%u\t\n",b);
scanf("%d",&b);
printf("\n%u\t",b);
//printf("%d\t",a);
a = b;
printf("%d\t",a);
return 0;
}
OUTPUT
Enter the integer value
55555555555555555555555555555555555555555
a= -477218589 b= 3817748707
55555555555555555555555555555555555555555
a= -477218589 b= 3817748707 Press any key to continue . . .
Friday, March 25, 2011
Macro Program
# include "stdio.h"
#define MAX(a, b) a>b ? a:b
int main()
{
int m, n;
m =20+ MAX(2, 3);
n = 2 * MAX(3, 2);
printf("m = %d, n = %d\n", m, n);
return 0;
}
OUTPUT:
m = 2, n = 3
Press any key to continue . . .
#define MAX(a, b) a>b ? a:b
int main()
{
int m, n;
m =20+ MAX(2, 3);
n = 2 * MAX(3, 2);
printf("m = %d, n = %d\n", m, n);
return 0;
}
OUTPUT:
m = 2, n = 3
Press any key to continue . . .
Wednesday, March 23, 2011
What is Quine?
/*A program that produces its complete source code as its only output is called a quine.*/
# include "stdio.h"
# include "windows.h"
int main()
{
FILE *fRead;
char ch;
fRead = fopen("\Quine.c","r");
if(fRead == NULL)
MessageBox(0,"Karthik","Please Check the Source ile path",16);
while((ch=fgetc(fRead) )!= NULL)
{
printf("%c",ch);
}
return 0;
}
OUTPUT:
# include "stdio.h"
# include "windows.h"
int main()
{
FILE *fRead;
char ch;
fRead = fopen("\Quine.c","r");
if(fRead == NULL)
MessageBox(0,"Karthik","Please Check the Source ile path",16);
while((ch=fgetc(fRead) )!= NULL)
{
printf("%c",ch);
}
return 0;
}
# include "stdio.h"
# include "windows.h"
int main()
{
FILE *fRead;
char ch;
fRead = fopen("\Quine.c","r");
if(fRead == NULL)
MessageBox(0,"Karthik","Please Check the Source ile path",16);
while((ch=fgetc(fRead) )!= NULL)
{
printf("%c",ch);
}
return 0;
}
OUTPUT:
# include "stdio.h"
# include "windows.h"
int main()
{
FILE *fRead;
char ch;
fRead = fopen("\Quine.c","r");
if(fRead == NULL)
MessageBox(0,"Karthik","Please Check the Source ile path",16);
while((ch=fgetc(fRead) )!= NULL)
{
printf("%c",ch);
}
return 0;
}
A power B calculation
# include "stdio.h"
double what( double , int );
int main()
{
int nNumber1,nNumber2;
int nLoop1,nLoop2;
printf("Enter the two number you want to display\n");
scanf("%d%d",&nNumber1,&nNumber2);
//Type casting from the double to integer
printf("A power B : %d \n",(int)what(nNumber1,nNumber2));
return 0;
}
double what( double z, int y)
{
double answer = 1;
while( y > 0 )
{
if( y%2 == 1)
answer = answer * z;
y=y/2;
z=z*z;
}
return answer;
}
OUTPUT:
Enter the two number you want to display
10 3
A power B : 1000
Press any key to continue . . .
double what( double , int );
int main()
{
int nNumber1,nNumber2;
int nLoop1,nLoop2;
printf("Enter the two number you want to display\n");
scanf("%d%d",&nNumber1,&nNumber2);
//Type casting from the double to integer
printf("A power B : %d \n",(int)what(nNumber1,nNumber2));
return 0;
}
double what( double z, int y)
{
double answer = 1;
while( y > 0 )
{
if( y%2 == 1)
answer = answer * z;
y=y/2;
z=z*z;
}
return answer;
}
OUTPUT:
Enter the two number you want to display
10 3
A power B : 1000
Press any key to continue . . .
Control Satement in C language
/*
Write a program to print
1
2 2
3 3 3
4 4 4 4
5 5 5 5 5.
*/
# include "stdio.h"
int main()
{
int nNumber;
int nLoop1,nLoop2;
printf("Enter the last number you want to display\n");
scanf("%d",&nNumber);
for(nLoop1=1;nLoop1<=nNumber;nLoop1++)
{
for(nLoop2 = nLoop1;nLoop2 > 0; nLoop2--)
{
printf("%d \t",nLoop1);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
OUTPUT:
Enter the last number you want to display
10
1
2 2
3 3 3
4 4 4 4
5 5 5 5 5
6 6 6 6 6 6
7 7 7 7 7 7 7
8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8
9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9
10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10
Press any key to continue . . .
Write a program to print
1
2 2
3 3 3
4 4 4 4
5 5 5 5 5.
*/
# include "stdio.h"
int main()
{
int nNumber;
int nLoop1,nLoop2;
printf("Enter the last number you want to display\n");
scanf("%d",&nNumber);
for(nLoop1=1;nLoop1<=nNumber;nLoop1++)
{
for(nLoop2 = nLoop1;nLoop2 > 0; nLoop2--)
{
printf("%d \t",nLoop1);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
OUTPUT:
Enter the last number you want to display
10
1
2 2
3 3 3
4 4 4 4
5 5 5 5 5
6 6 6 6 6 6
7 7 7 7 7 7 7
8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8
9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9
10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10
Press any key to continue . . .
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)